We’re going to learn about the different parts of speech, which are like special groups that words belong to. They help us understand how words work together to make sentences. Imagine that words have jobs, just like people do! We’ll explore these different jobs in simple and easy words, so it’s perfect for beginners learning English. From action words that show what we do to words that describe things and people, we’ll cover it all. Get ready to discover how these parts of speech make English come alive! Let’s get started!
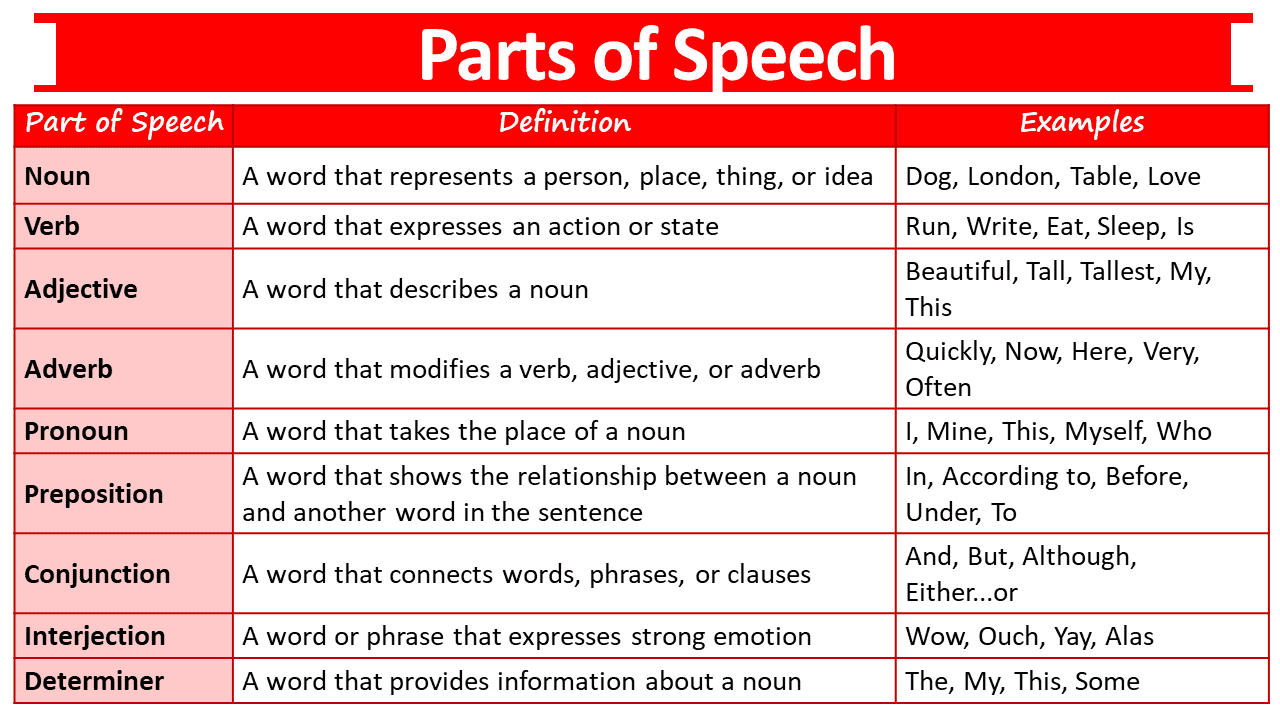
Nouns: Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They can be concrete or abstract. Examples of nouns include person, city, book, and love. Nouns help us identify and describe the world around us.
Types of Nouns
- Common Nouns: cat, house, car, city
- Proper Nouns: Mary, London, Toyota, Statue of Liberty
- Concrete Nouns: table, dog, flower, book
- Abstract Nouns: love, happiness, courage, knowledge
- Countable Nouns: apple, chair, friend, book
- Uncountable Nouns: water, music, advice, happiness
- Collective Nouns: family, team, flock, herd
Verbs: Verbs are action words that express what someone or something does. They convey actions, occurrences, or states of being. Examples of verbs include run, sing, eat, and is. Verbs give life to sentences and show us what is happening.
Types of Verbs
- Action Verbs: run, eat, sing, dance
- Transitive Verbs: write a letter, kick the ball, paint a picture
- Intransitive Verbs: sleep, laugh, cry, walk
- Linking Verbs: is, become, feel, seem
- Modal Verbs: can, may, must, should
- Helping Verbs: have, had, do, will
Adjectives: Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns. They provide more information about the qualities, characteristics, or attributes of the nouns they modify. Examples of adjectives include happy, beautiful, tall, and delicious. Adjectives make our descriptions vivid and engaging.
Types of Adjectives
- Descriptive Adjectives: big, beautiful, happy, intelligent
- Demonstrative Adjectives: this, that, these, those
- Possessive Adjectives: my, your, his, her
- Comparative Adjectives: taller, faster, smarter, more beautiful
- Superlative Adjectives: tallest, fastest, smartest, most beautiful
Adverbs: Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They describe how, when, where, or to what extent an action or state occurs. Examples of adverbs include quickly, very, here, and almost. Adverbs add depth and precision to our sentences.
- Adverbs of Time: now, yesterday, later, always
- Adverbs of Place: here, there, everywhere, nowhere
- Adverbs of Manner: quickly, gently, happily, slowly
- Adverbs of Degree: very, quite, too, extremely
- Adverbs of Frequency: often, sometimes, rarely, never

Pronouns: Pronouns are words used in place of nouns. They help us avoid repetition and make our sentences flow smoothly. Examples of pronouns include he, she, they, and it. Pronouns simplify our language and allow for more efficient communication.
Types of Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Possessive Pronouns: mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
- Demonstrative Pronouns: this, that, these, those
- Reflexive Pronouns: myself, yourself, himself, herself
- Interrogative Pronouns: who, whom, what, which
- Indefinite Pronouns: everyone, someone, nobody, anything
Prepositions: Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in the sentence. They indicate location, direction, time, or manner. Examples of prepositions include on, in, at, and before. Prepositions help us understand the spatial and temporal relationships in our sentences.
Types of Preposition
- Simple Prepositions: in, on, at, by
- Compound Prepositions: according to, because of, in front of, instead of
- Prepositions of Time: before, after, during, until
- Prepositions of Place: under, above, beside, between
- Prepositions of Direction: to, from, into, onto
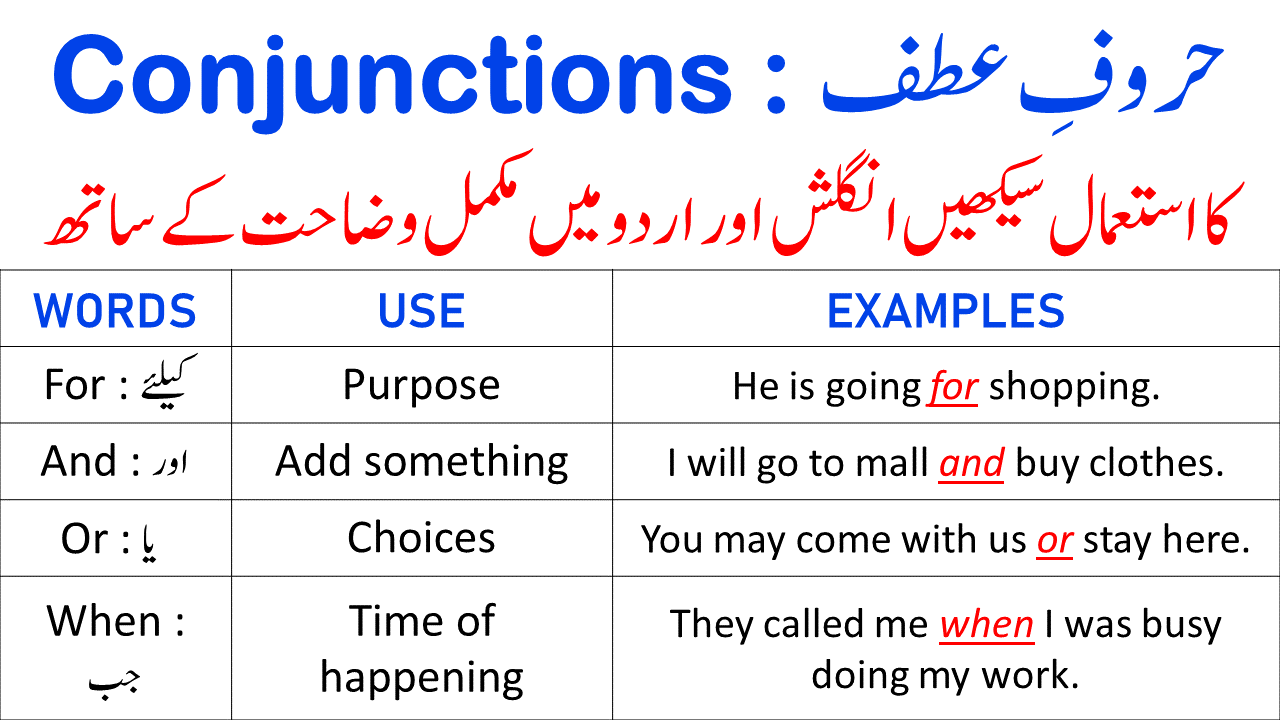
Conjunctions: Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They join ideas, coordinate thoughts, or show relationships between words or groups of words. Examples of conjunctions include and, but, or, and because. Conjunctions make our sentences cohesive and coherent.
Types of Conjunctions
- Coordinating Conjunctions: and, but, or, so
- Subordinating Conjunctions: although, because, while, if
- Correlative Conjunctions: either…or, neither…nor, both…and
Interjections: Interjections are short exclamations or words that express strong emotions or reactions. They are used to convey surprise, joy, anger, or other intense feelings. Examples of interjections include wow, oh, ouch, and hurray. Interjections add emotion and emphasis to our expressions.
Articles: Articles are small words (a, an, the) that come before nouns to indicate whether they are general or specific. The article “a” or “an” is used for non-specific nouns, while “the” is used for specific nouns. Articles help us clarify the noun’s reference in a sentence.
Determiners: Determiners are words that provide information about the specificity or quantity of a noun. They include words like “this,” “that,” “each,” “every,” and “some.” Determiners help us specify or quantify the noun they modify.
Types of Determiners
- Articles: a, an, the
- Possessive Determiners: my, your, his, her, our, their
- Demonstrative Determiners: this, that, these, those
- Quantifiers: some, many, few, several