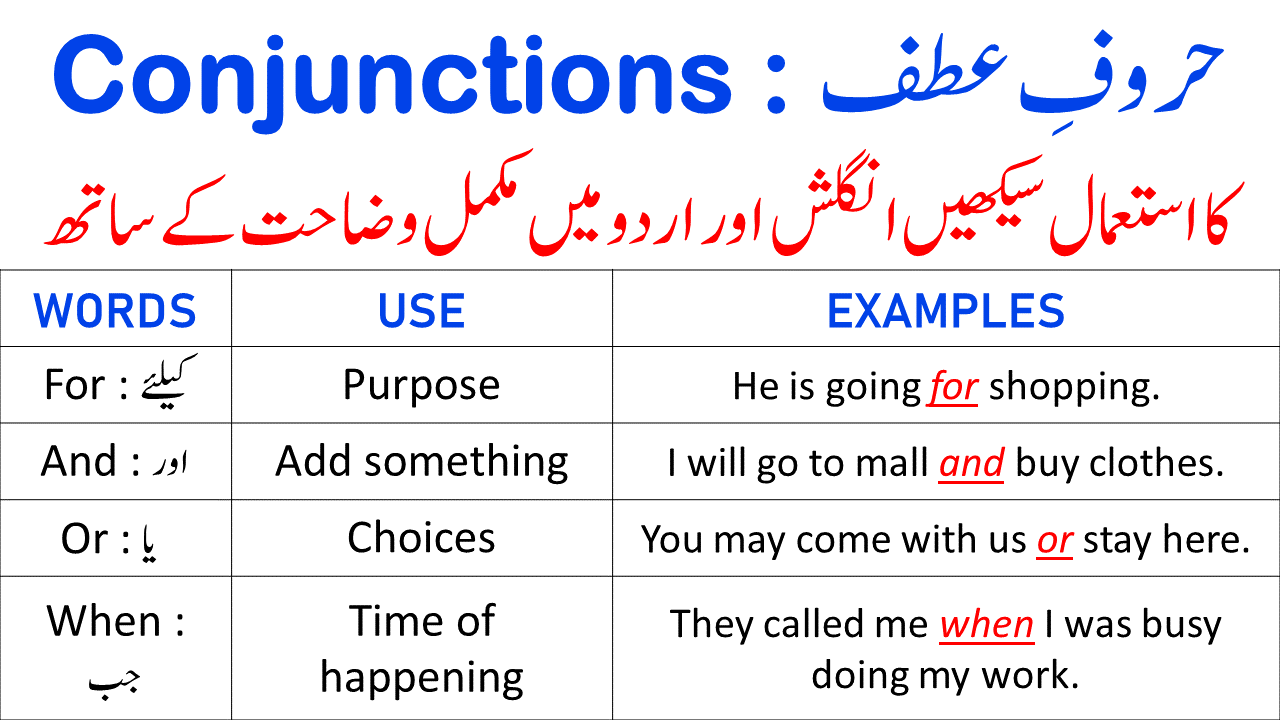
What are conjunctions? The word which joins two parts of a sentence is called a conjunction. It is one of the important parts of speech. It joins two or more sentences, phrases, and independent clauses.
Learn conjunctions definition, examples, and rules of conjunctions in English grammar.
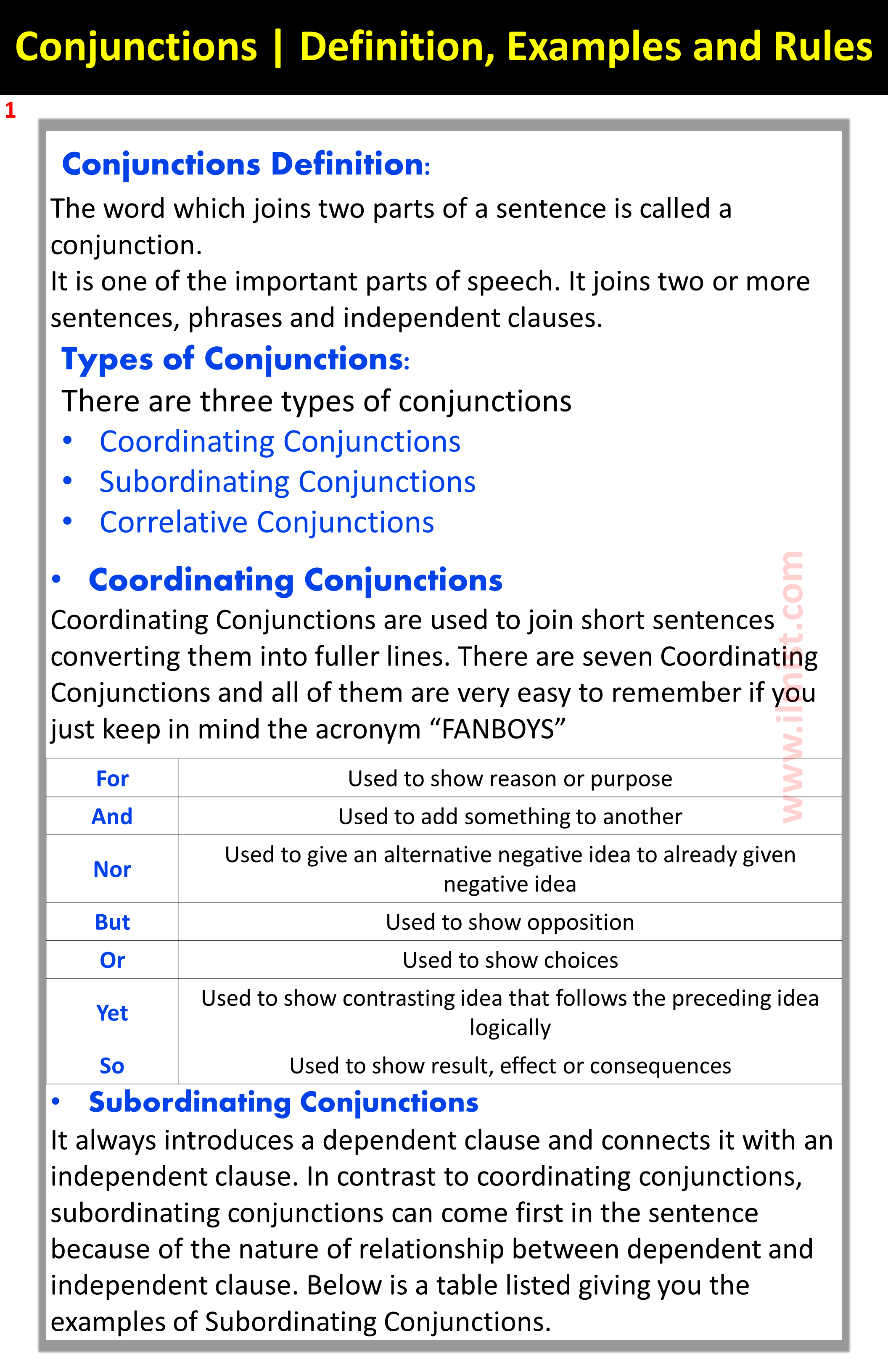
Conjunctions Definition:
The word which joins two parts of a sentence is called a conjunction.
Note: Download the PDF book of this lesson at the bottom of this page.
Types of Conjunctions
There are three types of conjunctions
- Coordinating Conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunctions
- Correlative Conjunctions
- Coordinating Conjunctions:
Coordinating Conjunctions are used to join short sentences converting them into fuller lines. There are seven Coordinating Conjunctions and all of them are very easy to remember if you just keep in mind the acronym “FANBOYS”.
| For | Used to show reason or purpose |
| And | Used to add something to another |
| Nor | Used to give an alternative negative idea to an already given negative idea |
| But | Used to show opposition |
| Or | Used to show choices |
| Yet | Used to show a contrasting idea that follows the preceding idea logically |
| So | Used to show result, effect, or consequences |
- Subordinating Conjunctions:
It always introduces a dependent clause and connects it with an independent clause. In contrast to coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions can come first in the sentence because of the nature of the relationship between dependent and independent clauses. Below is a table listed giving you examples of Subordinating Conjunctions.
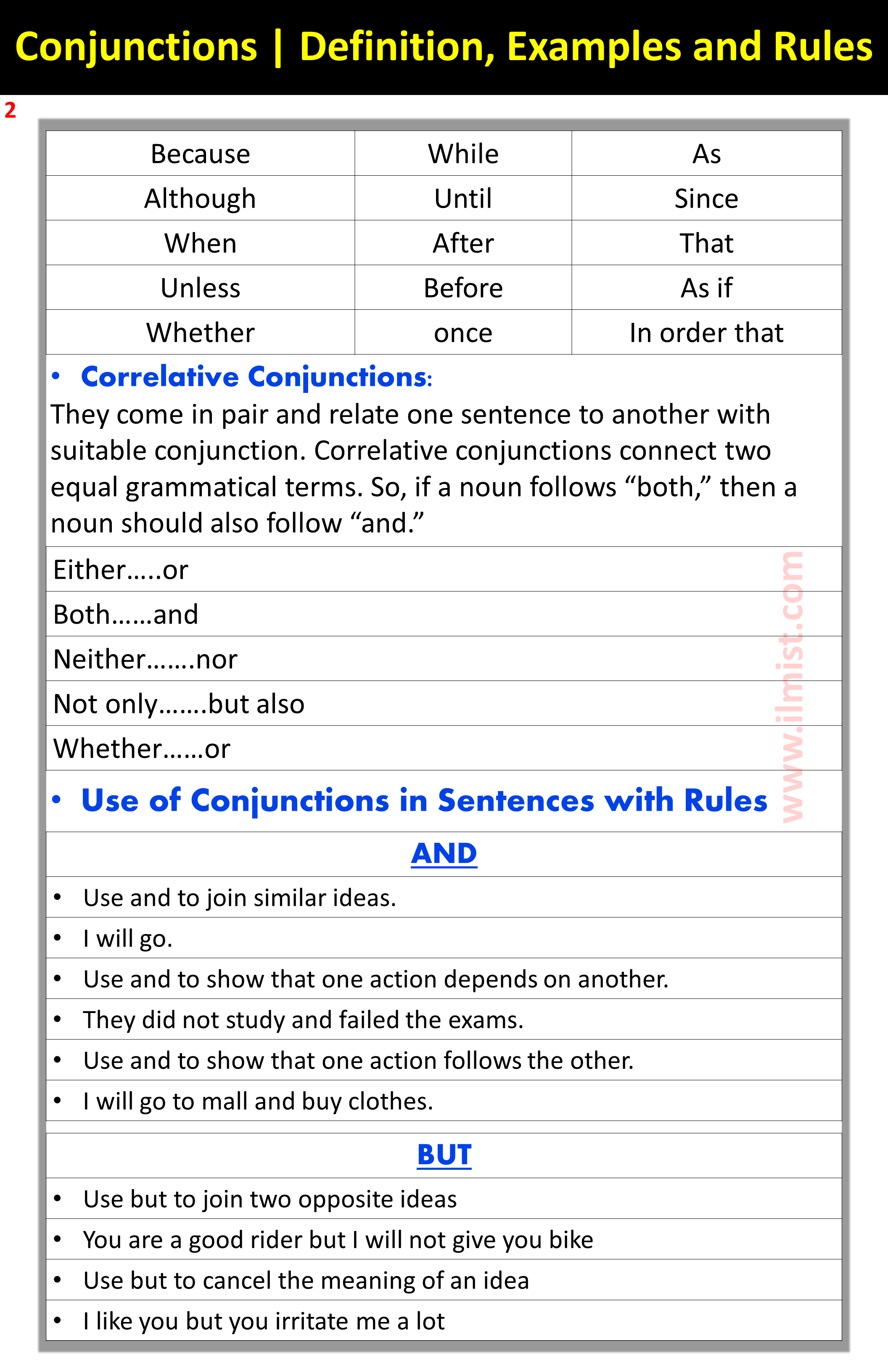
| Because | While | As |
| Although | Until | Since |
| When | After | That |
| Unless | Before | As if |
| Whether | once | In order that |
- Correlative Conjunctions:
They come in pairs and relate one sentence to another with suitable conjunction. Correlative conjunctions connect two equal grammatical terms. So, if a noun follows “both,” then a noun should also follow “and.”
|
|
|
|
|
Use of Conjunctions in Sentences with Rules:
| AND |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| BUT |
|
|
|
|
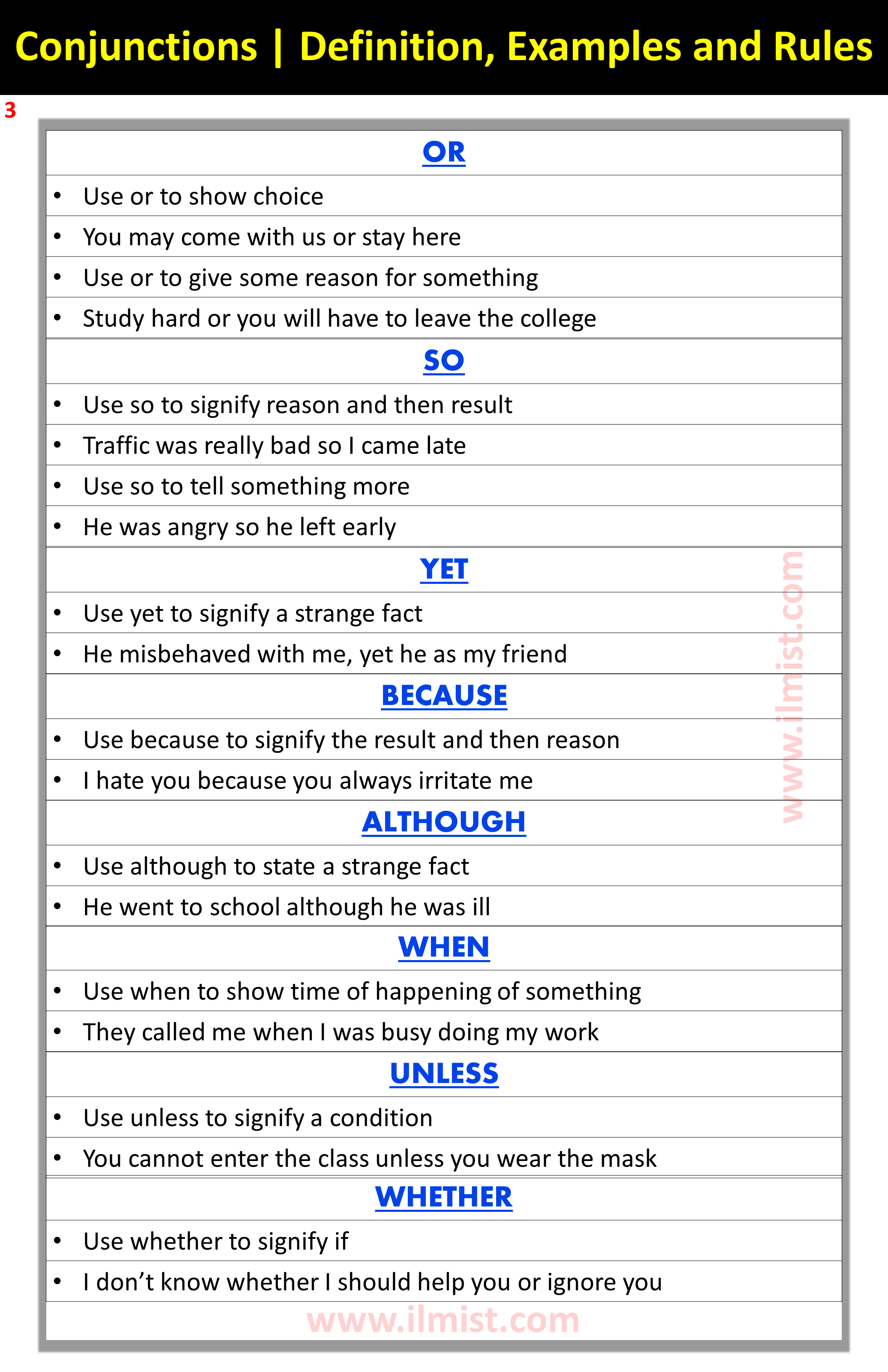
| OR |
|
|
|
|
| SO |
|
|
|
|
| YET |
|
|
| BECAUSE |
|
|
| ALTHOUGH |
|
|
| WHEN |
|
|
| UNLESS |
|
|
| WHETHER |
|
|
| WHILE |
|
|
| UNTIL |
|
|
| AFTER |
|
|
| BEFORE |
|
|
| ONCE |
|
|
| AS |
|
|
| SINCE |
|
|
| THAT |
|
|
| AS IF |
|
|
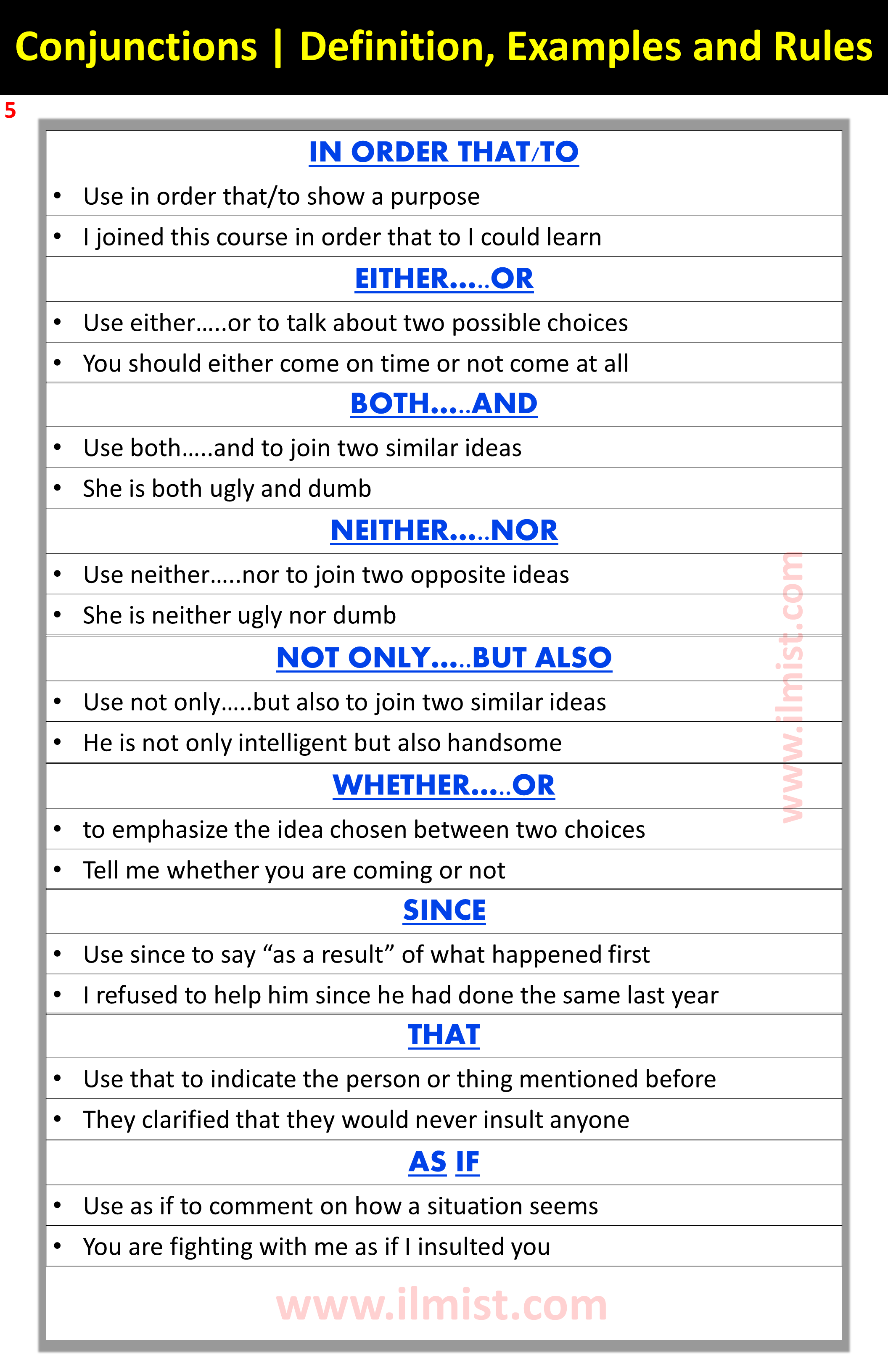
| IN ORDER THAT/TO |
|
|
| EITHER…..OR |
|
|
| BOTH…..AND |
|
|
| NEITHER…..NOR |
|
|
| NOT ONLY…..BUT ALSO |
|
|
| WHETHER…..OR |
|
|
 Click here to Download PDF Book
Click here to Download PDF Book
Conjunctions | Definition, Examples, and Rules